Subnetting in networking with example
Subnetting is the process of dividing a single large IP network into multiple smaller, logical sub-networks called subnets.
Core Concepts
- IP Address Components: An IPv4 address (32 bits) consists of two main parts: the Network ID (identifies the overall network) and the Host ID (identifies a specific device).
- Subnet Mask: A 32-bit number used to define where the network part ends and the host part begins. For example,
255.255.255.0indicates that the first 24 bits are for the network. - CIDR Notation: A shorthand for the subnet mask. For example,
/24means the first 24 bits are network bits. - Borrowing Bits: Subnetting works by “borrowing” bits from the Host ID portion to create the Subnet ID.
Formulas
- Number of Subnets:
2n2 to the n-th power2𝑛, where
nn𝑛 is the number of borrowed bits.
- Number of Hosts per Subnet:
2h−22 to the h-th power minus 22ℎ−2, where
hhℎ is the number of remaining host bits.
- The “- 2” accounts for the Network Address (first) and Broadcast Address (last), which cannot be assigned to devices.
Step-by-Step Example
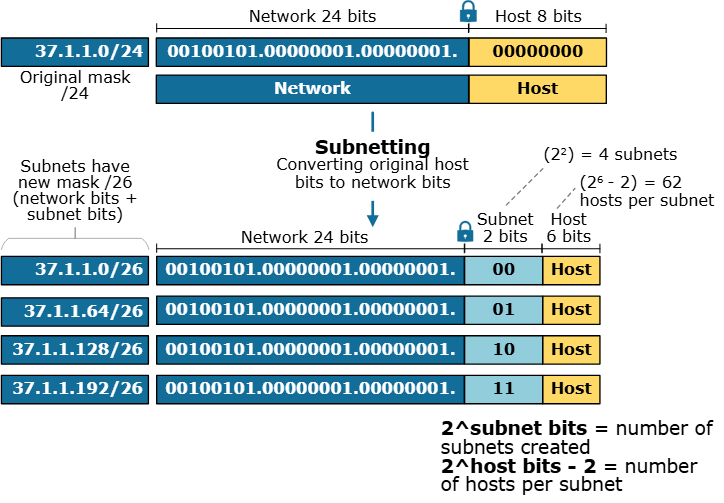
Scenario: You have the network 192.168.1.0/24 and need to divide it into 4 equal subnets.
- Identify Current State:
- Network:
192.168.1.0 - Subnet Mask:
255.255.255.0(/24) - Total available host bits: 8 (
32−24=832 minus 24 equals 832−24=8).
- Network:
- Calculate Borrowed Bits:
- To get 4 subnets, solve
2n≥42 to the n-th power is greater than or equal to 42𝑛≥4.
n=2n equals 2𝑛=2 bits. You must borrow 2 bits from the host portion.
- To get 4 subnets, solve
- Find New Subnet Mask:
- New Network bits:
24+2=2624 plus 2 equals 2624+2=26.
- CIDR: /26
- Decimal Mask:
255.255.255.192(The last octet bits11000000equals 192).
- New Network bits:
- Determine Subnet Ranges:
- Each subnet will have
26=642 to the sixth power equals 6426=64 total addresses (32 total bits – 26 network bits = 6 host bits).
- Subnet 1: 192.168.1.0 – 192.168.1.63 (Usable: .1 to .62)
- Subnet 2: 192.168.1.64 – 192.168.1.127 (Usable: .65 to .126)
- Subnet 3: 192.168.1.128 – 192.168.1.191 (Usable: .129 to .190)
- Subnet 4: 192.168.1.192 – 192.168.1.255 (Usable: .193 to .254)
- Each subnet will have
Benefits of Subnetting
- Reduced Congestion: Limits broadcast traffic to a smaller “domain”.
- Enhanced Security: Allows administrators to isolate departments (e.g., HR from Sales).
- Efficient IP Usage: Prevents wasting thousands of addresses in large class-based networks.