What is SD-WAN in networking?
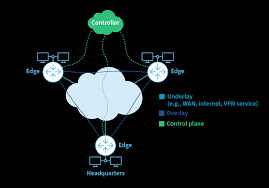
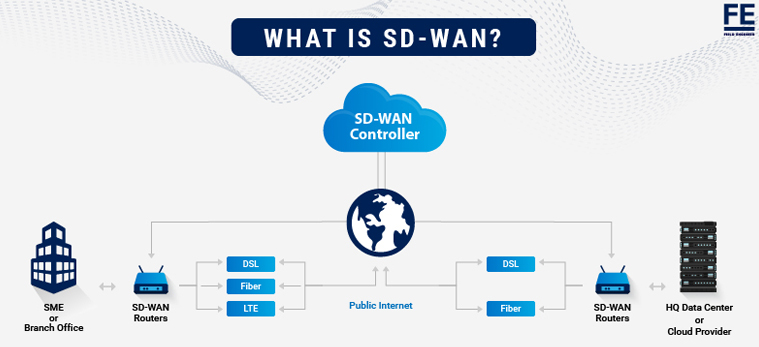
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is a virtualized networking approach that uses software to manage and optimize connectivity between geographically dispersed locations, such as branch offices, data centres, and cloud environments
Core Components
- SD-WAN Edge: Physical or virtual appliances at branch sites, data centers, or cloud locations that forward traffic based on policies and real-time link health.
- SD-WAN Orchestrator: A centralized management tool for configuring, monitoring, and applying policies across all SD-WAN nodes from a single dashboard.
- SD-WAN Controller: The “brain” of the network that makes routing decisions based on pre-defined business policies and real-time conditions.
Key Features
- Transport Independence: Works across any combination of transport services, including MPLS, broadband internet, 5G, and satellite.
- Application-Aware Routing: Identifies applications (like Zoom or Salesforce) and prioritizes them to ensure high performance for critical business functions.
- Dynamic Path Selection: Constantly monitors link metrics (latency, jitter, packet loss) and automatically steers traffic to the best available path.
- Zero-Touch Provisioning (ZTP): Allows for rapid deployment by automatically configuring new devices once they are connected to a WAN link, reducing the need for on-site IT staff.
- Major Benefits
- Cost Savings: Reduces reliance on expensive private MPLS circuits by leveraging cheaper broadband and cellular connections.
- Enhanced Cloud Performance: Eliminates the need to “backhaul” all cloud-bound traffic to a central data center, reducing latency for SaaS applications.
- Simplified Management: Replaces manual, device-by-device configuration with centralized, automated policy enforcement.
- Integrated Security: Often includes built-in next-generation firewalls (NGFW), encryption, and is a foundational component of SASE (Secure Access Service Edge).
- Are you considering SD-WAN to replace a traditional MPLS network, or are you primarily looking to improve cloud application performance?
- Major Benefits
- Cost Savings: Reduces reliance on expensive private MPLS circuits by leveraging cheaper broadband and cellular connections.
- Enhanced Cloud Performance: Eliminates the need to “backhaul” all cloud-bound traffic to a central data center, reducing latency for SaaS applications.
- Simplified Management: Replaces manual, device-by-device configuration with centralized, automated policy enforcement.
- Integrated Security: Often includes built-in next-generation firewalls (NGFW), encryption, and is a foundational component of SASE (Secure Access Service Edge).